Are Creatine Monohydrate Supplements Just for Bodybuilders?
Are Creatine Monohydrate Supplements Just for Bodybuilders?
Are Creatine Monohydrate Supplements Just for Bodybuilders?
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound that is found in small amounts in meat and fish. It is also produced by the body in small quantities from the amino acids arginine, glycine, and methionine. Creatine is stored in the muscles and used as a source of energy during high-intensity exercise.
On the other hand, creatine monohydrate is a popular dietary supplement used to enhance overall health, athletic performance, and muscle growth. Despite its widespread use in the fitness industry, there is still a lot of confusion and misconceptions surrounding this supplement. One of the most common misconceptions is that creatine monohydrate is only beneficial for bodybuilders and weightlifters, and not for the average person.
In this blog, we will explore the truth about DoNotAge's creatine monohydrate supplement and their potential benefits beyond just muscle building. We will look at the science behind this supplement, its benefits, and drawbacks, and who can benefit from using it. So, if you are curious about creatine monohydrate and want to learn more about its potential uses, benefits, and safety, then keep reading.

Creatine Supplements Boosts the Body’s ATP Production
There are several benefits of taking creatine monohydrate supplements. Creatine monohydrate is naturally produced in our bodies at around 1 gram per day. Once creatine supplements have been taken, they are transformed into phosphocreatine by an enzyme called creatine kinase. This converts the creatine monohydrate into phosphocreatine.
We naturally have phosphocreatine in our body. A 70KG (155lbs) man has 120g of phosphocreatine. 40% is the unphosphorylated form, this simply means it does not have a phosphate group attached to it. Whilst the phosphorylated creatine is used in energy metabolism (to be discussed later) unphosphorylated creatine is thought to have beneficial effects too. The positive effects of unphosphorylated creatine include improved cognitive function, reduction of inflammation, and it may even act as an antioxidant (to be discussed) link to the part of the blog that mentions this. This suggests that creatine shouldn’t just be taken to boost exercise performance! It also helps to protect cells from damage and inflammation. Additionally, 60% of the 120g of creatine is creatine phosphate. This is important for the bodies ATP/PC energy system.
Just like is the case with NAD+, we produce creatine naturally but in low levels. Regarding the body’s natural creatine stores, only 1-2% is broken down and used each day, equating to only 1.2-2.4g each day being used by our bodies. By supplementing creatine, these levels can significantly rise, equating to more energy for our bodies.
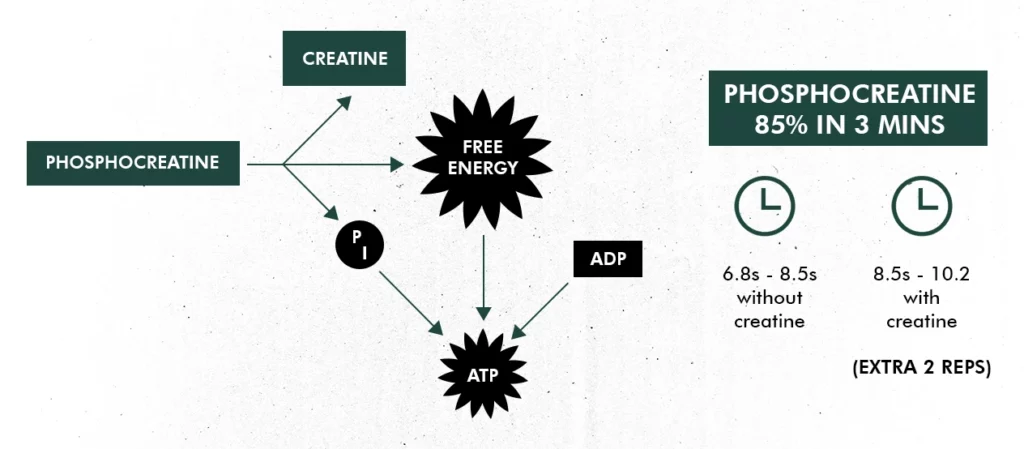
As shown in the diagram below, a benefit of taking creatine monohydrate supplements is having more energy for longer periods of time.
Before we use the ATP/PC energy system:
- We have adenosine triphosphate in the body which is one adenosine molecule and three phosphate molecules (ATP).
- Then, the enzyme ATPase is used to break ATP into adenosine diphosphate (ADP - 2 phosphates instead of 3) and free energy lasting 1-2 seconds.
- Because this only releases energy for 1-2 seconds, we need to use an energy system to expand this energy.
Adenosine Triphosphate/Phosphocreatine (ATP/PC) energy system without Creatine supplements:
- Phosphocreatine is broken down by the enzyme creatine kinase into creatine, phosphate (this breaks off from ATP, making ADP), and energy.
- When this phosphate molecule is broken off, it produces energy that typically lasts for 8-10 seconds.
ATP/PC System With Creatine:
- When you supplement creatine monohydrate, this increases the concentration of the body’s creatine stores, which leads to a quicker resynthesis of ATP during high-intensity exercise.
- This leads to energy for a longer period of time. Instead of 8-10 seconds, it will be 10-12 seconds.
Extra Information Regarding the ATP/PC Energy System:
Once this reaction has taken place, it takes 10 minutes for the ATP/PC system to replenish, and 3 minutes for it to replenish to 85%. This will give you energy for 6.8s – 8.5s without creatine and 8.5s – 10.2s with creatine. This is the reason why powerlifters rest for around 3 minutes in between their heavy sets at the gym! This system only works when we are working anaerobically (flat out without the use of oxygen e.g., when doing very heavy sets at the gym).
Can You Take Creatine Without Working Out?
A commonly known benefit of supplementing creatine monohydrate is that it increases the amount of water that is stored in the muscles. This is due to the fact that creatine draws water into the muscle cells, increasing their volume and making them look fuller and more pumped. This is sometimes referred to as cell swelling.
The mechanism behind this is relatively simple. When creatine is stored in the muscles, it attracts water molecules through a process called osmosis. Osmosis is the movement of water from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration. The arrival of water into the muscle cells increases their size and volume, this makes your muscles look more impressive.
However, aside from the well-known benefits of the supplement. We will discuss the benefits it has on everyday life!
Creatine Monohydrate Improves Cognitive Function
Research has found that supplementing creatine monohydrate may help to enhance cognitive brain function, particularly in older adults. One study on creatine supplements found that creatine monohydrate supplementation benefitted memory and recall in healthy adults between 66-76 years old. What’s more, another study showed that creatine improved cognitive performance and reduced mental fatigue in young adults during a demanding task.
Also, as discussed, creatine increases ATP. The brain requires a significant amount of ATP to function optimally, and some research suggests that creatine supplementation can enhance ATP production in the brain, leading to improved cognitive function.
Another way that creatine monohydrate can improve cognitive function is by increasing the availability of energy to the brain. This can enhance memory, attention, and other cognitive processes that require high levels of energy.
Several studies on creatine supplementation have also shown that creatine supplementation can improve cognitive function in certain populations, such as vegetarians and vegans who have lower natural levels of creatine in their bodies. Other studies also found that creatine can improve cognitive function in older adults and individuals with certain neurological conditions.
Can Creatine Reduce Inflammation?
Inflammation is a natural response of the body to injury or infection, but when it becomes chronic, it can lead to health problems like heart disease, arthritis, and cancer. Creatine may help reduce inflammation by suppressing the production of molecules called cytokines that are involved in the inflammatory response.
Creatine may also have antioxidant properties, which means it helps to reduce damage to cells caused by molecules called free radicals. Free radicals can contribute to inflammation, so by reducing their activity, creatine can help reduce inflammation in the body.
Can Creatine Improve Your Mental Health?
Creatine supplementation may increase levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, including dopamine and serotonin, which are involved in regulating mood. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that is associated with pleasure and reward, and low levels have been linked to depression and other mood disorders. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that is involved in regulating mood, sleep, and appetite, and low levels have been associated with depression and anxiety.
Studies have found that creatine supplementation can increase levels of dopamine and serotonin in the brain, which may contribute to improved mood. For example, a study published in the Journal of Psychiatric Research found that creatine supplementation improved symptoms of depression in women with major depressive disorder who were also taking an antidepressant medication.
Another theory is that creatine may have antioxidant properties that help to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain. Inflammation and oxidative stress have been linked to mood disorders and other neurological conditions, and by reducing these factors, creatine may help to improve mood and cognitive function.
Creatine Supplements Increase Muscle Strength and Power
This allows you to lift heavier weights for more reps and perform more explosive movements. This is one of the reasons why creatine monohydrate supplements are popular amongst gym-goers. However, benefits of creatine monohydrate supplements do not just apply to gym-goers. Studies have also shown that creatine monohydrate can also lead to an increase in power output for other anaerobic sports such as sprinting, shot-put, long-jump etc. As well as increasing muscle mass via an increase in energy to muscle cells, creatine also activate a signalling pathway which is involved in regulating muscle protein synthesis. By activating this pathway, creatine can help to promote the synthesis of new muscle proteins, leading to increased muscle size and strength.

Creatine Monohydrate Supplements Increase Muscle Recovery Times
If you’re someone that is active, creatine monohydrate supplements may benefit you as creatine supplements speed up recovery time bouts of intense exercise. This happens by preventing muscle damage from occurring when training. Intense exercise has been proven to cause micro-tears in muscle fibres, leading to muscle soreness and inflammation. A benefit of creatine monohydrate supplements is the fact that these negative effects can be reduced, allowing for a faster recovery and less soreness after exercise.
Studies on benefits of creatine monohydrates supplements have found that markers of muscle damage 24 hours and 48 hours after exercise were lower in groups of people who were supplementing creatine monohydrate than those who were not. This was also the same for delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS), the measures were lower for the group of people supplementing creatine monohydrate than those who were not.
Reduced Risk of Injury with Creatine
As mentioned, prior creatine monohydrate supplements can enhance collagen mRNA. Collagen can lead to increased bone density, means fewer brittle bones. Therefore, this reduces the risk of bone fractures.
As well as this, when we exercise our body produces harmful substances called reactive oxygen species (ROS). These ROS can damage our cells and tissues which can cause inflammation, leading to chronic conditions. But creatine has been shown to have antioxidant properties, meaning it can neutralise these harmful substances and prevent damage to our cells and tissues. This means that creatine can help to reduce inflammation and promote healing after an injury. This lowers the risk of further injuries.
There are lots of questions and confusion around creatine and some of its effects. We will now answer frequently asked questions and debunk any myths along the way.
Is There a Loading Phase for Creatine?
Whist you could just take 10g of creatine monohydrate a day, it is common for trainers to normally supplement 20-25g of creatine for 5-7 days and then back down to 3-5g afterwards.
Why Creatine Load?
Studies on creatine loading have found that supplementing creatine at a rate of 20g/day for 6 days resulted in a 20% increase in muscle total creatine concentration. The rationale behind creatine loading is that saturates the muscles with creatine helping the body to quickly increase its stores of ATP. After 5-7 days we would recommend going to a maintenance level of 10g per day with DoNotAge.org’s creatine monohydrate. Research has also shown that if you load creatine monohydrate supplements for 5 days, it can increase collagen mRNA by 250%. Collagen mRNA is a type of messenger that carries the generic information required to produce collagen proteins. As discussed in a previous blog, collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body.
Should I Take Creatine on Rest Days?
it is recommended to take creatine monohydrate supplements consistently every day to maintain elevated levels in the muscles. Creatine is a supplement that works by increasing the amount of creatine stored in the muscles, which helps to improve energy production during high-intensity exercise.
While it is true that rest days are important for muscle recovery and growth, taking creatine on these days can help to maintain the elevated levels of creatine in the muscles, which may provide additional benefits for muscle performance and recovery.
How Long Does Creatine Take to Work?
Creatine can start working in as little as a few days to a week, depending on several factors. When you start taking creatine, your muscles will begin to accumulate more creatine, which can help to improve your energy production during high-intensity exercise.
However, the exact timeline for seeing the benefits of creatine can vary depending on several factors, such as your current fitness level, your training regimen, and your diet. Some people may notice improvements in their strength and performance within the first week of taking creatine, while others may take several weeks to see noticeable improvements.
In general, it is recommended to take creatine monohydrate supplements such as DoNotAge.org’s creatine monohydrate for at least 4-6 weeks to see the full benefits of the supplement. After this initial period, you can continue to take creatine as part of your daily routine to maintain elevated levels in your muscles.
How Long Does Creatine Stay in Your System?
Creatine typically stays in your system for several days to weeks, depending on several factors. When you take creatine, it is absorbed into your bloodstream and transported to your muscles, where it is stored as phosphocreatine.
The half-life of creatine in your body is approximately three hours, which means that after three hours, half of the creatine you have consumed will have been eliminated from your body. However, it is important to note that the effects of creatine can last longer than its half-life, as the creatine stored in your muscles can continue to provide benefits for several weeks.
The duration of creatine in your system can also depend on the amount and frequency of your creatine intake. Taking a higher dose of creatine or taking it more frequently can lead to higher levels of creatine in your muscles, which can take longer to clear from your system.
How Much Water Should I Drink on Creatine?
There is no specific amount of water that you need to drink while taking creatine, but it's important to stay adequately hydrated. Creatine works by increasing the amount of water that your muscles hold, so it's important to drink enough water to support this process.
A general guideline for daily water intake is to drink at least 2 litres of water per day. However, if you're taking creatine, you may need to drink more water than this to support the increased water retention in your muscles. Aim to drink at least 2.5 litres of water per day whilst taking creatine. It's also important to note that excessive water intake can be dangerous, so don't overdo it.
Does Creatine Cause Hair Loss?
There is currently no scientific evidence to suggest that creatine monohydrate supplements causes hair loss in healthy individuals. While some anecdotal reports have suggested a possible link between creatine use and hair loss, these reports are not supported by clinical research.
Hair loss is a complex condition that can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, hormonal imbalances, stress, and nutritional deficiencies. Creatine is a naturally occurring substance found in many foods, and it plays a critical role in energy metabolism and muscle function. While creatine supplementation has been shown to increase muscle mass and improve athletic performance, there is no evidence to suggest that it directly causes hair loss.
When Is the Best Time to Take Creatine Monohydrate?
Although there are different opinions on the best times to creatine monohydrate, the most important thing is to take it consistently and in the recommended doses. With that being said here are recommended timings for taking creatine monohydrate:
Pre-workout
Some athletes prefer to take creatine monohydrate supplements before their workout to increase energy and power output during exercise. Taking it with a carbohydrate-containing beverage may enhance its absorption.
Post-workout
Taking creatine monohydrate after a workout may help to replenish energy stores and improve recovery.
Loading Phase
For people that choose to do a loading phase, they may take a higher dose of creatine monohydrate for the first few days to saturate their muscles with creatine before transitioning to a maintenance dose.
Is Pre-Workout Creatine?
Pre-workout and creatine are not the same. Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found in muscle tissue that helps to supply energy for high-intensity exercise. It is commonly used as a dietary supplement to increase muscle mass, strength, and power output during exercise. Creatine supplements typically contain creatine monohydrate, which is the most well-researched and effective form of creatine.
Pre-workout supplements, on the other hand, are typically formulated to provide a combination of ingredients that can help to improve athletic performance, increase energy, and reduce fatigue during exercise. While some pre-workout supplements may contain creatine, they may also contain other ingredients such as caffeine, beta-alanine, nitric oxide boosters, or amino acids.
Pre-workout supplements may contain creatine, but not all pre-workout supplements contain this ingredient. Pre-workout supplements are typically formulated to provide a combination of ingredients that can help to improve athletic performance, increase energy, and reduce fatigue during exercise.
Some pre-workout supplements may contain creatine monohydrate as one of the main ingredients, as it has been shown to improve power output and muscle strength during high-intensity exercise. Other pre-workout supplements may contain alternative forms of creatine or other ingredients that are purported to enhance athletic performance, such as caffeine, beta-alanine, or nitric oxide boosters.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are several benefits of creatine monohydrate supplements. That makes it a popular and effective way to enhance overall health as well as athletic performance and muscle mass. Research has shown that creatine supplementation is safe for most individuals and can provide significant benefits when used appropriately.
If you are interested in trying creatine monohydrate supplements, it's important to choose a high-quality product from a reputable source. Here at DoNotAge.org we offer a range of premium-quality supplements at the best prices, including creatine monohydrate powder. Our creatine supplement is formulated with pure, micronized creatine monohydrate powder that is easily absorbed and utilised by the body.
By choosing DoNotAge.org’s creatine monohydrate, you can feel confident that you are getting a safe and effective product that can help you to achieve your fitness and health goals. So why wait? Take action today and start experiencing the benefits of creatine supplementation for yourself!